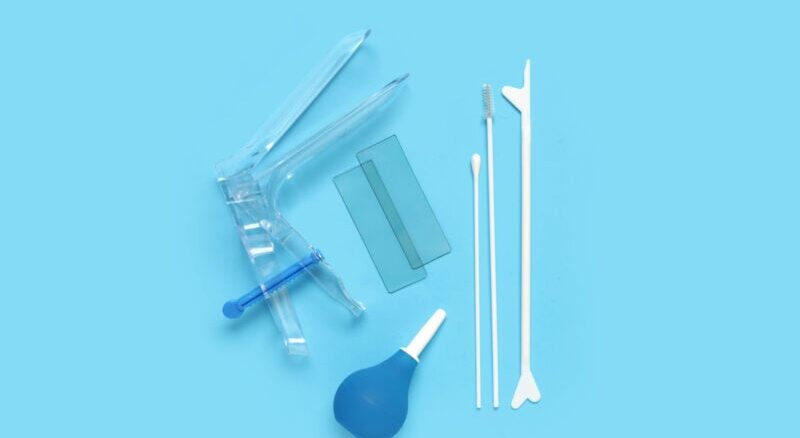
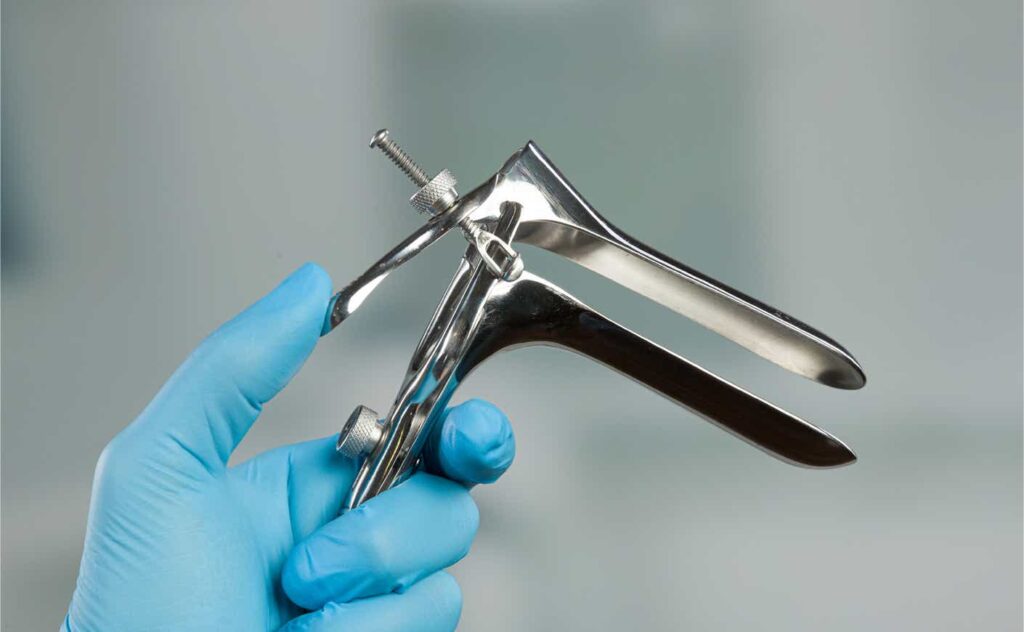
The Pap smear, or Pap test, is one of the most important diagnostic exams in women’s health, aimed at the early detection of cervical cancer (cervix) and other cellular abnormalities in this area. This test is particularly useful for detecting human papillomavirus (HPV) infections and precancerous cellular changes that could lead to cancer. The primary goal of the Pap smear is to identify cellular changes before cancer develops, enabling early treatment. This article will cover the process, importance, and interpretation of Pap smear results.
What is a Pap Smear?
The Pap smear is a simple, painless diagnostic test conducted during a pelvic exam by a doctor or a trained midwife. During the test, cervical cells are collected and sent to a laboratory for analysis to check for any possible cellular changes. This test is particularly important because it can detect cervical cancer-related cellular changes before the disease progresses. These changes are usually caused by HPV infection, one of the most significant risk factors for cervical cancer.
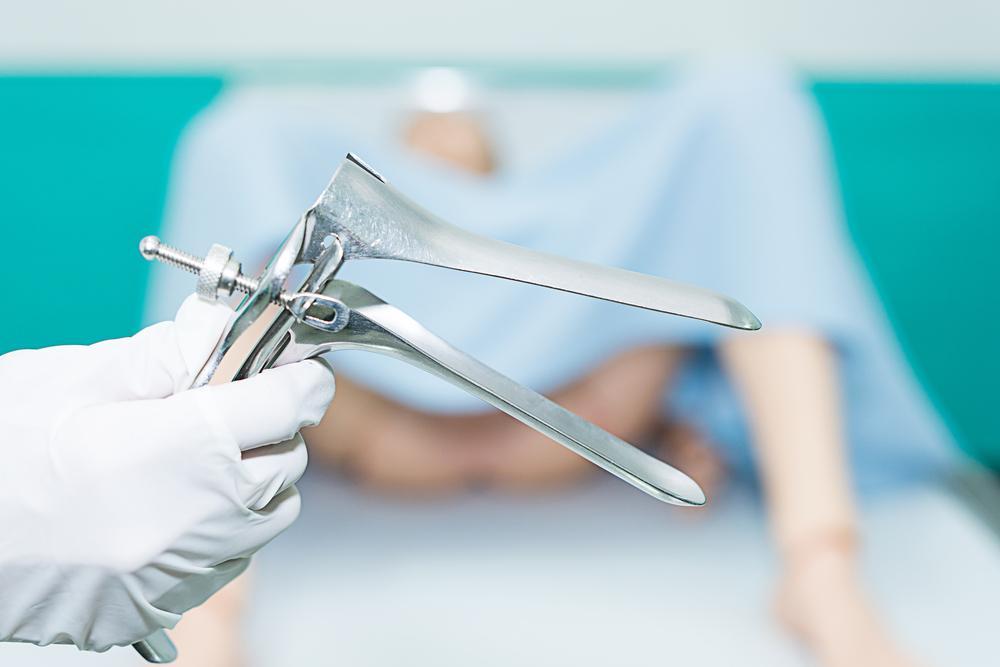
The Importance of a Pap Smear
Cervical cancer is one of the most common cancers in women worldwide, but regular Pap smears can prevent the disease from developing or detect it in its early stages. The primary benefits of a Pap smear include:
- Early Cancer Detection: This test can identify precancerous cellular changes, enabling treatment in the early stages.
- Detection of Viral Infections, Such as HPV: This virus can cause abnormal cellular changes, ultimately leading to cervical cancer.
- Cancer Prevention: Detecting and treating cellular changes before they become cancerous can save many women’s lives.
When Should a Pap Smear Be Done?
It is recommended that women between the ages of 21 and 65 undergo a Pap smear every three years. However, in certain cases, such as a family history of cancer or an HPV infection, the doctor may recommend shorter intervals. Factors that may indicate the need for more frequent Pap smears include:
- Weak Immune System: Individuals with conditions like HIV or those taking immunosuppressive medications may need more frequent testing.
- Use of Specific Medications: Certain drugs, like steroids, may impact cervical cellular health.
- History of Abnormal Test Results: Individuals with abnormal results in previous tests may require more frequent follow-up.

How to Prepare for a Pap Smear
Proper preparation can help improve the accuracy of Pap smear results. Important tips to follow before the test include:
- Avoid Sexual Intercourse: Abstain from sex 24 to 48 hours before the test.
- Avoid Tampons, Creams, and Vaginal Medications: Do not use tampons, contraceptive creams, or vaginal medications at least 48 hours before the test.
- Schedule During a Non-Menstrual Period: Try to have the test when you are not menstruating, as bleeding may affect the results.
Steps in a Pap Smear Procedure
The Pap smear is a quick, simple procedure performed during a pelvic exam. The steps include:
- Pelvic Examination: The doctor or midwife will ask you to lie down on the exam table with your legs in special supports.
- Use of a Speculum: The doctor will use a speculum to open the vaginal walls, allowing clear visibility of the cervix.
- Sample Collection: Using a small brush or specialized instrument, the doctor collects a sample of cervical cells. This may be slightly uncomfortable but is usually painless.
- Sending the Sample to the Laboratory: The collected cells are sent to a laboratory for detailed analysis.
What to Expect After a Pap Smear
After a Pap smear, you may experience mild discomfort or light bleeding, which is usually temporary. If bleeding lasts more than a few days or you feel severe pain, consult your doctor. Pap smear results are typically available within one to two weeks, and your doctor will discuss the results with you.
Interpreting Pap Smear Results
Pap smear results are reported as either “normal” or “abnormal.” Understanding these results can provide valuable information about your cervical health.
- Normal Results: If the results are normal, it means your cervical cells are healthy, with no abnormal or precancerous changes observed. In this case, the doctor usually recommends repeating the test after three years.
- Abnormal Results: Abnormal results do not necessarily mean cancer but may indicate precancerous changes or viral infections. These changes fall into two main categories:
- Mild Changes (ASCUS): These are usually minor changes often due to HPV infections. In such cases, the doctor may recommend an HPV test or a repeat Pap smear for a closer look.
- Severe Changes (LSIL and HSIL): These may indicate the presence of precancerous cells. The doctor may recommend additional tests, like colposcopy or biopsy, in these cases.
Next Steps for Abnormal Results
If your results are abnormal, your doctor may suggest the following for further investigation:
- HPV Test: This test checks for HPV infection, which can cause cellular changes and ultimately lead to cancer.
- Colposcopy: In this procedure, the doctor examines the cervix more closely using a magnifying instrument called a colposcope. If abnormalities are seen, a biopsy may be performed.
- Biopsy: In this method, a small sample of cervical tissue is sent to the laboratory for further examination.
The Difference Between Pap Smear and HPV Test
While the checks for cellular changes in the cervix, the HPV test specifically detects human papillomavirus (HPV). This virus is a major cause of cellular changes and cervical cancer. The HPV test can be performed alongside the Pap smear, and if an HPV infection is detected, further follow-up may be needed.
Cervical Cancer and HPV
Cervical cancer is usually caused by chronic HPV infections. Most HPV infections clear on their own without causing harm, but in some cases, long-term infection can lead to cellular changes and ultimately cancer. Pap smears and HPV tests can help detect these changes early.
Conclusion
The Pap smear is one of the most important and effective tests for identifying precancerous changes and cervical cancer. This test helps women detect cellular changes early and receive appropriate treatment to prevent cervical cancer from developing. Regular Pap smears, combined with HPV testing, are the best way to prevent cervical cancer and protect women’s health.
Consultation with a Specialist
For a Pap smear and accurate interpretation of its results, you can consult Dr. Azarmidokht Shojaei, a specialist in gynecology, obstetrics, and infertility. With her expertise and specialized knowledge, she provides top-quality diagnostic and treatment services. You can also schedule a consultation or make an online appointment through her website or by calling the clinic.