Genital warts are one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs), caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). This condition affects both men and women, leading to small, soft growths on the genital and anal areas. Some types of HPV can increase the risk of various cancers, such as cervical, vaginal, penile, anal, and even throat cancer. In this article, we will provide a thorough overview of genital warts, their causes, symptoms, prevention methods, and effective treatments for combating the virus.
What Are Genital Warts?
Genital warts are small, sometimes clustered, growths that appear on the genital, anal, and occasionally oral areas. These warts are usually soft and flesh-colored, but they can be slightly darker. While they are often painless, they may cause itching, burning, or discomfort in some cases. The infection is transmitted through direct skin contact, including sexual contact, and can occur at any age.
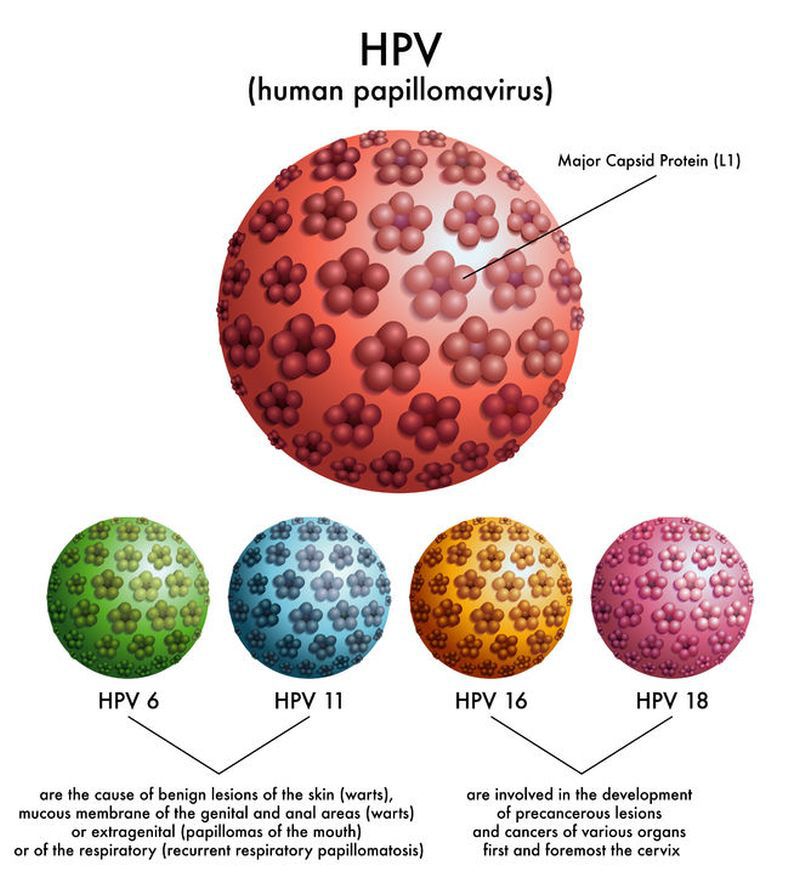
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and Its Types
HPV has over 100 different types, around 40 of which affect the genital and anal areas. The primary types responsible for genital warts are HPV-6 and HPV-11. However, high-risk types like HPV-16 and HPV-18 can increase the risk of cervical cancer and other cancers related to the genital and anal regions.
Causes of Genital Warts
The main cause of genital warts is HPV, which spreads through close skin contact with infected areas, particularly during sexual activity. Vaginal, anal, or even oral sex can lead to the transmission of the virus. It is possible to contract HPV even without visible symptoms, as an infected individual may not have warts but can still carry and spread the virus.
Modes of HPV Transmission
The primary mode of HPV transmission is through skin-to-skin contact in the genital areas, which can occur during vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Sharing personal items like towels or underwear can rarely spread the virus. It’s important to note that while condoms can reduce the risk, they do not provide complete protection since HPV can spread through uncovered skin.
Symptoms of Genital Warts
Genital warts may be very small and sometimes not visible to the naked eye. Common symptoms include:
- Soft, flesh-colored growths: Warts may appear singly or in clusters.
- Itching or burning: Some individuals may experience itching or burning in the wart area.
- Pain or discomfort: Warts may be painful when touched or during intercourse.
- Bleeding: Minor bleeding can occur if warts are irritated or damaged.
Genital Warts in Women
In women, genital warts may appear on the internal and external genital areas, including the vagina, cervix, vulva, and anus. Some warts may be located inside the vagina or on the cervix, making them invisible to the naked eye, but they can be detected during a pelvic exam or through sexual activity.
Genital Warts in Men
In men, genital warts can appear on various areas, such as the penis, scrotum, and anus. These warts can be singular or clustered, and in some cases, may cause discomfort during urination or sexual activity.
Diagnosis of Genital Warts
Genital warts are usually diagnosed through a physical examination by a healthcare professional. If the warts are too small to be seen, a specialist may use a colposcope for a more detailed examination. For women, a Pap smear can help detect HPV in the cervix.

Preventing Genital Warts
The best ways to prevent and HPV include vaccination and practicing safe sex. Effective prevention methods are:
- HPV vaccination: The HPV vaccine, such as Gardasil, can prevent infections with types of HPV that cause genital warts and cancer. It’s recommended for individuals aged 9 to 26.
- Condom use: Using condoms can reduce the risk of HPV transmission, although it does not offer full protection.
- Limiting sexual partners: Having a monogamous relationship or fewer sexual partners can lower the risk.
- Sexual health education: Awareness of HPV transmission and practicing safe sex can help reduce risks.
Effective Treatments for Genital Warts
Although genital warts can sometimes resolve on their own, many individuals seek treatment due to discomfort, appearance, or to prevent spreading the virus. Several treatments include medications and physical removal methods.
Medication Treatments:
- Topical creams: Medications like imiquimod (Aldara), podofilox (Condylox), and sinecatechins (Veregen) boost the immune system to fight the virus.
- Trichloroacetic acid (TCA): This chemical is used to destroy wart cells and is typically applied in a healthcare setting.
Physical Treatments:
- Cryotherapy (freezing): This method involves freezing the warts with liquid nitrogen, causing them to fall off.
- Laser therapy: A laser is used to burn away the warts, suitable for larger or more resistant growths.
- Electrocautery: This procedure uses an electric current to burn off warts and may require local anesthesia.
- Surgery: Large or treatment-resistant warts may be surgically removed.
Risks and Complications of HPV
HPV poses a significant risk of developing cancers in the genital and anal regions. High-risk HPV types can damage cells and lead to cervical, penile, anal, and throat cancers. HPV vaccination can prevent many of these risks, and regular Pap smears help in early detection.
HPV and Pregnancy
this can develop or worsen during pregnancy due to hormonal changes and increased blood flow to the genital area. If warts become large enough to obstruct childbirth, a cesarean section may be recommended. Transmission from mother to newborn is rare.
HPV and Men
While men are less likely than women to develop HPV-related cancers, they can still contract genital warts and certain types of cancer. HPV vaccination is recommended for men, especially those with multiple partners or same-sex relationships.
Diagnostic Methods for HPV
In women, Pap smears and HPV DNA tests can help identify HPV infections and precancerous changes. In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to determine the specific type of HPV and assess the warts’ condition.
Conclusion
Genital warts are a common STI caused by HPV. They can appear as small, barely noticeable growths or cause severe symptoms such as itching and burning. The best prevention is through vaccination and safe sex practices. There are various treatment options for managing genital warts, which should be discussed with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate approach.
Consulting a Specialist
For diagnosis and treatment of genital warts or sexual health advice, you can consult Dr. Azarmidokht Shojaei, a specialist in gynecological surgery and infertility. Dr.Shojaei provides expert diagnostic and therapeutic services. You can also schedule an appointment online for added convenience.